Latest Logpresso-based content with thanks to @jgstew and @strawgate
Update: Monday, 12/20/2021 15:45 UTC
Good Monday morning, BigFix’ers, it’s been a busy weekend for us as I’m sure it has been for many of you. We have lots of content updates to announce and summarize today.
All Logpresso / Log4jscan content is use at-your-own-risk
Analysis to collect the results of the Logpresso scan utility:
- bigfix-content/analyses/log4j2-scan results.bes at main · jgstew/bigfix-content · GitHub
This Analysis provides results regardless of the Logpresso scan content used below - same analysis whether you scan with the prebuilt binaries, JAR scan using the installed Java, or JAR scan using a temporary JRE.
Significant updates on the Analysis to retrieve results of the logpresso-log4jscan process were made over the weekend.
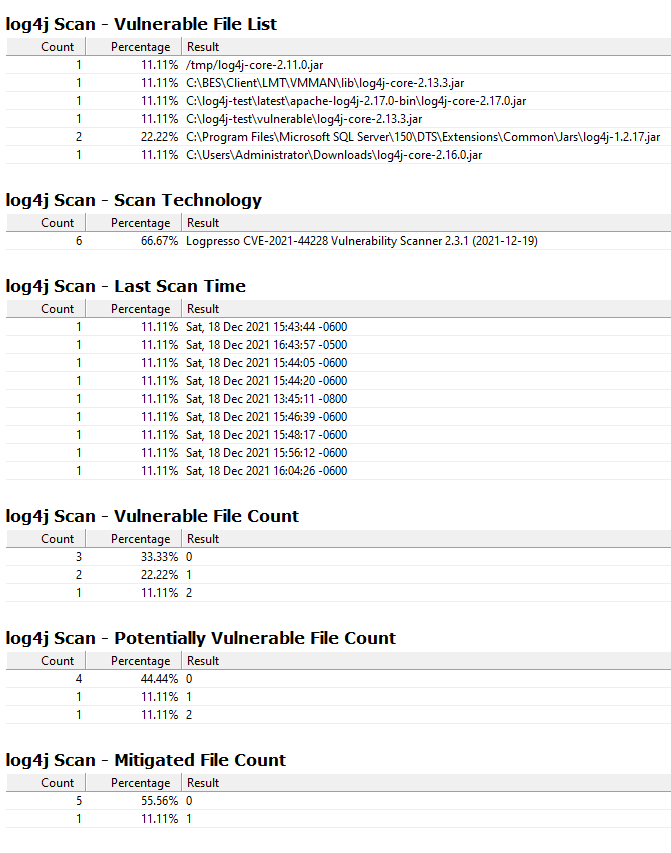
The property list is expanded to include
- log4j Scan - Vulnerable File List
- log4j Scan - Scan Technology
- log4j Scan - Last Scan Time
- log4j Scan - Vulnerable File Count
- log4j Scan - Potentially Vulnerable File Count
- log4j Scan - Mitigated File Count
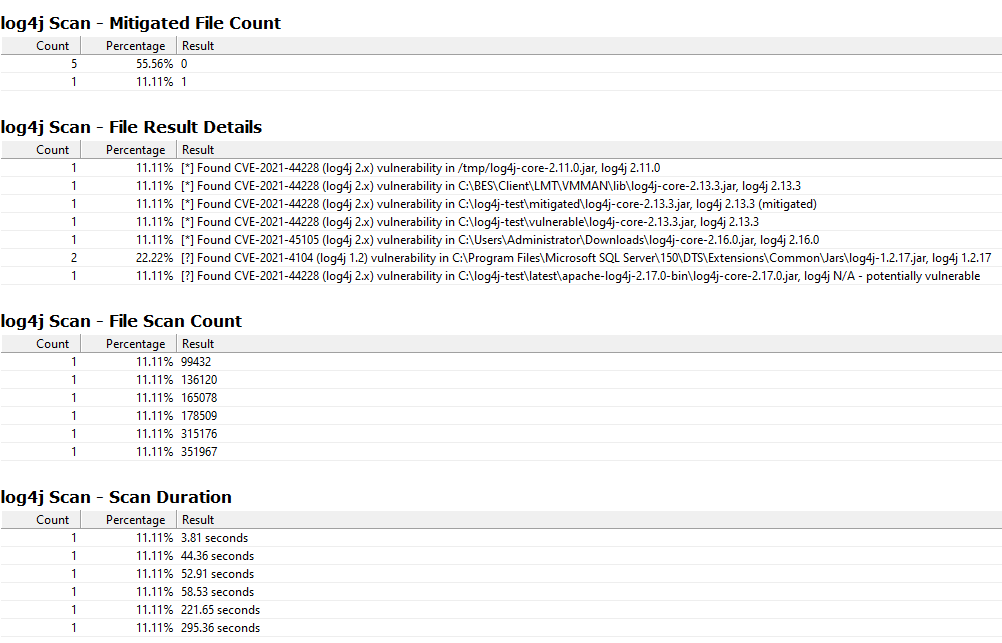
- log4j Scan - File Result Details
- log4j Scan - File Scan Count
- log4j Scan - Scan Duration
The “File Scan Count” and “Scan Duration” are useful in identifying failed scans or scans that may have included network paths - a scan with 0 files or empty result probably failed to execute, and a scan with a long duration may have crossed network paths or scanned very large filesystems.
The “Scan Technology” entry includes the Logpresso-Log4jscan version that was executed.
The “File result details” entry contains the full line from the logfile, including the version of Log4j-core that the Logpresso scanner recognized, if any.
Scanning Tasks
The Scan Task falls into three categories:
-
Execute the Logpresso/Log4jScan utility using a native binary - currently built for Windows x64, Linux x64, and MacOS X
** Advantages: Smaller Downloads
** Disadvantages: Library dependencies; some reports of missing C++ runtimes on Windows, or glibc version on Linux.
Content:- Windows: bigfix-content/fixlet/Logpresso log4j2-scan - Windows x64.bes at main · jgstew/bigfix-content · GitHub
- Linux x64: bigfix-content/fixlet/Logpresso log4j2-scan - Linux x64.bes at main · jgstew/bigfix-content · GitHub
- Mac: bigfix-content/fixlet/Logpresso log4j2-scan - MacOS x64.bes at main · jgstew/bigfix-content · GitHub
-
Execute the Logpresso/Log4jScan JAR version using a native installed JRE on the endpoint. This requires at least JRE 7 to be found in the system PATH.
** Advantages: Less to download, more compatible across operating systems. With this method we’ve scanned Solaris and Raspbian!
** Disadvantages: Requires a JRE to be previously-installed.
Content:- Universal Scan with System JRE: bigfix-content/fixlet/Logpresso log4j2-scan - Universal.bes at main · jgstew/bigfix-content · GitHub
-
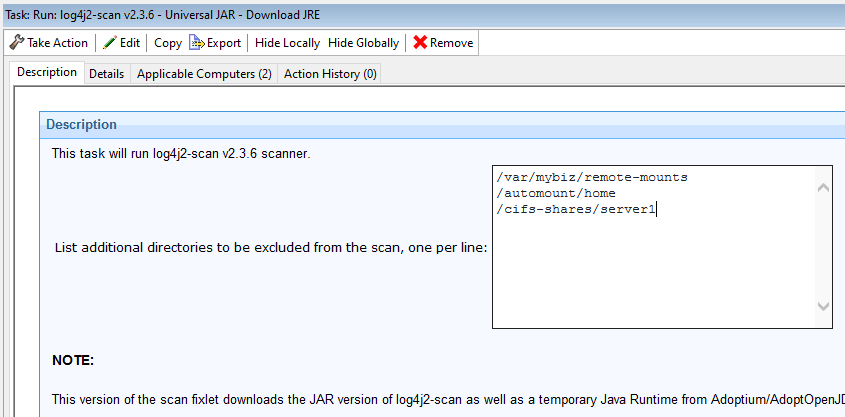
Download a temporary JRE to run the Logpresso/Log4jScan JAR. Currently we are providing custom fixlets for Windows x32, Windows x64, Linux x64, and Mac. Additional OS support coming soon. In our content, we are downloading the latest build of Adoptium (formerly AdoptOpenJDK) JRE 8. After the scan, the extracted JRE is deleted but the cached download is preserved (in it’s “sha1-name” form, not directly usable/vulnerable)
** Advantages: Supports more operating systems than the native binary scan, fewer OS library dependencies.
** Disadvantages: Larger downloads, support for additional operating systems requires additional JRE downloads added to the scan task. Have not found a Linux x32-based JRE that we can freely download and use (please post to the Megathread discussion if you know of one!)
Content:- Universal Scan with Temporary JRE: bigfix-content/fixlet/Logpresso Log4j2-scan - Universal - JRE.bes at main · jgstew/bigfix-content · GitHub
Common to all these methods are some known challenges & risks. While both log4jscan itself, and our Fixlet Content, are making efforts to avoid scanning network-mounted paths and symlinks, we cannot guarantee that those exclusions are completely effective. Especially on UNIX & Mac systems, it can be difficult to determine whether a filesystem is local or remote in a generalized way, as the OS hides some of those details from the user/process; and in the case of technologies like Automount, those remote filesystems may not even appear until they are accessed. Please Note that the Linux, Mac, and Java-based scans include the ability to add your own filesystem exclusion paths in the Description tab of the fixlet. These paths are added to our own list of generated exclusions when executing the scan.
More Community Content
In parallel, longtime guru and contributor @strawgate and Verve Industrial are producing content for low-impact scans. Rather than scanning the entire filesystem, their unique approach starts by checking which files are in use by a process - which can perform much faster/more-frequent scans that can help show where you’re most vulnerable. That content is described at Free Tools: Multiple Log4j Detection Mechanisms + Remediation . Be sure to check that out and evaluate whether Verve’s solutions are right for your. In particular in at least some areas he’s running ahead of our content on Remediation.
Forward Plans
-
We will be refreshing the Scan content frequently as new versions of Log4jscan are released. The current content is based on Log4jscan 2.3.6; 2.3.7 has already been released, adding even more network filesystems to the default exclusions, and we will be building for that version shortly. There have been five version releases in the last 24 hours.
-
We are asking for community members to let us know about their experiences with the scanning content that is available today. In particular, we need to hear if any of this is still scanning over network paths where we want to prevent scans from overwhelming shared fileservers. We have not had reports of scans traversing the network since much earlier releases.
-
We are planning to add more JRE runtimes for the “Download a Temporary JRE”-based scans. Please let us know in the Megathread which OS’s you need to see the most.
-
Planning to add use-at-your-own-risk remediation. Log4jscan itself can open the vulnerable JAR file and remove the vulnerable JndiLookup.class file, leaving the vulnerabilities at least partially remediated. We are also planning content to replace the log4j-core-X.jar file entirely with the latest Apache Log4j version (while retaining the old version’s filename).
– Either of these methods carries significant risks of breaking your applications, and where possible you should follow guidance from your software providers on remediating their products; however taking no action at all can also expose serious vulnerabilities. Whether to patch or replace the Log4j libraries is a risk-based decision that we all must make for our own platforms.
Please provide feedback on your testing, especially any refinements you would recommend for excluding obvious network drives or other folders you think should be excluded on Linux or Windows here: Log4j CVE-2021-44228 Detection and Mitigation
For tips on how to download files from GitHub, see Tips: Downloading files from GitHub